|
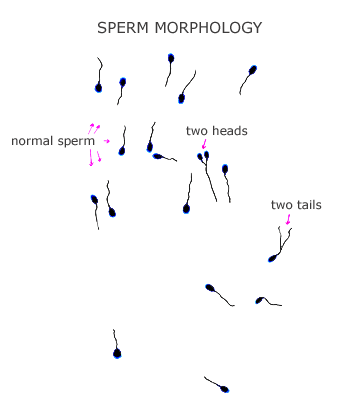
Human spermatozoa can be viewed for morphologic assessment using either a bright field microscope (after they have been fixed and stained) or a high quality phase contrast microscope (on wet prep of unstained sperm). The morphology (form or shape) of the sperm cells can then be classified as normal or abnormal.
The types of sperm defects that can be identified are often classified into groups including (1) head shape or size (large, small, tapered, amorphous, vacuolated, double headed); (2) neck or midpiece defects (absent tail, distended or thin midpiece); and (3) tail defects (short, multiple, broken, or coiled tails).
|

|